How does Client Payroll Manager pay for overtime?
These four options, and others related to overtime, can be found by going to Tools | Payroll System Options | Premium & Subsidy tab.
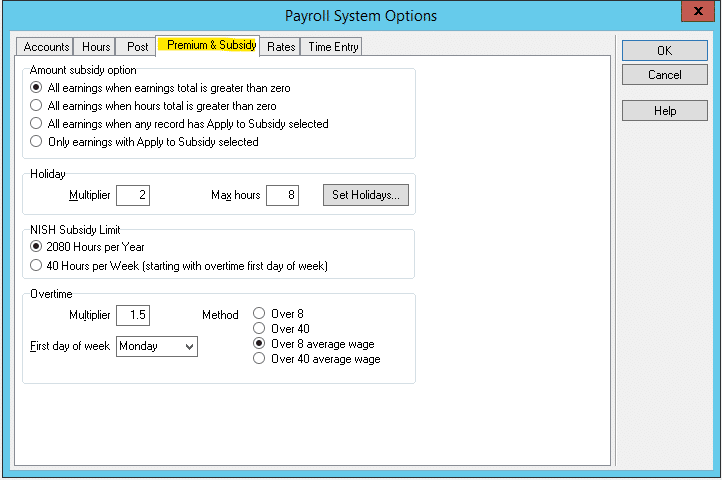
Select the Amount Subsidy Option from the options in the top section.
The other settings in the Overtime Section shown above include:
- Multiplier. This value defaults to 1.5, meaning overtime is paid as time-and-a-half. If time is to be paid at double-time, the value should be set at 2.0 and so on.
- First day of week: The day of the week that constitutes the start of a pay week. This is only relevant when using the Over 40 average wage option.
Which one should we be using?
Local or state regulations most often dictate which method should be used, so you will need to determine the proper setting based on your local regulations.
What are the differences between the four?
In terms of how each works, a detailed description and examples follow:
Over 8 / Over 40:
These are the most common and traditional methods of overtime pay. Both pay overtime in fundamentally the same way: overtime pay is calculated simply by taking the pay for the record and multiplying by the Payroll System Option’s Multiplier value.
Overtime is usually ‘time and a half’ (Multiplier = 1.5), meaning the pay for overtime is the pay for the normal work + half the pay for the normal work. For example, if a job pays $10 per hour and overtime is paid at time-and-a-half, the total pay for each hour of overtime work will be $15 per hour: $10 + ($10 * .5).
Presuming a time-and-a-half pay structure for overtime (in other words, Multiplier = 1.5), overtime for various different job payment methods is as follows:
Piece rate: The overtime premium is paid based on the amount of pay earned for the number of pieces produced. For example:
- One hour of overtime is indicated.
- During the overtime hour, 10 pieces were produced.
- The pay for those pieces totals $1.73.
Result: The overtime pay for the work would be 1.73 * .5 = $0.87.
Guaranteed rate: The overtime premium is based directly on the prevailing wage attached to the job step.
- One hour of overtime is indicated.
- The job pays a guaranteed hourly rate of $8.74.
Result: The overtime pay for the work would be 8.74 * .5 = $4.37
Regular (hourly) Based on productivity: The overtime premium is based on the prevailing wage X the employee’s rating for this step, work type or overall.
- One hour of overtime is indicated.
- The job has a prevailing wage of 8.74 and the employee is rated at 64%.
- The employee’s per hour earnings for the job would be 8.74 X 64% = $5.5936
Result: The overtime pay for the work would be 5.5936 * .5 = $2.80.
Regular (hourly) Based on average hourly rate: The overtime premium is based on the employee’s average hourly rate, as defined on the Wage Rates tab of Employee Setup.
- One hour of overtime is indicated.
- The employee has an average hourly rate of $3.09.
Result: The overtime pay for the work would be 3.09 * .5 = $1.55
Special rate: The overtime premium is based on the employee’s Special rate, as defined on the Wage Rates tab of Employee Setup.
- One hour of overtime is indicated.
- The employee has a special rate of $4.00.
Result: The overtime pay for the work would be 4.00 * .5 = $2.00
Based on a defined wage rate: The overtime premium is based on the wage rate in question, as defined on the Wage Rates tab of Employee Setup.
- One hour of overtime is indicated.
- The time in question was spent in a step that is attached to a Programmed Hours pay code.
- The job step is setup to pay based on the Calc method wage rate.
- The employee has a Programmed Hours rate of $6.47.
Result: The overtime pay for the work would be 6.47 * .5 = $3.24 Unpaid: The overtime is not paid.
Over 8 average wage:
In this case, the pay for overtime is calculated by determining the average hourly rate of pay earned over the course of the same day, then multiplying by the Multiplier value. Since a work day is typically 8 hours, this is considered the average wage ‘over 8 hours’ but in reality, the calculation of the average is done for all eligible work in a single day. This means that even hours that do not normally get paid at all will be paid an overtime premium if they are marked as overtime.
It’s important to remember the calculation of average wage earned over the course of the 8 hours can include unpaid time if the unpaid job step is associated with a pay code that is set to ‘Apply to overtime premium’. This is the setting that determines if work is eligible to be considered part of the calculated average.
For example, presume a person has the following time records for the day, that all of the work counts toward overtime pay calculation (based on each pay code’s ‘Apply to overtime premium’ option) and that the Multiplier value is 1.5 (time-and-a-half):
- 3 hours in piece rated work: $4.79.
- 2 hours in guaranteed rate work: $16.00
- 3 hours in productivity-based work: $18.72
- 1 hour in unpaid programmed time: $0.00. This is the hour that is marked as overtime.
The pay for the overtime hour of work would be $2.20:
- Total non-overtime earnings: 4.79 + 16 + 18.72 = 39.51
- Total overtime-eligible hours: 3 + 2 + 3 + 1 = 9
- 39.51 / 9 = 4.39 * .5 = 2.20
If we take the exact same work records but the unpaid time does not count toward the calculation of the overtime pay, the pay for the overtime hour would be $2.47:
- Total non-overtime earnings: 4.79 + 16 + 18.72 = 39.51
- Total overtime-eligible hours: 3 + 2 + 3 = 8
- Because the hour of unpaid time is not considered in the calculation of the overtime average rate, the duration of that record does not factor into the total.
- 39.51 / 8 = 4.93875 * .5 = 2.47
Over 40 average wage:
Like the over 8 average wage, the over 40 average wage determines the pay value for overtime based on the average hourly amount earned over time. The only difference is that the over 40 method calculates the average based on all of the work done in a week, rather than just one day. Like over 8 average, the over 40 average is only calculated based on overtime-eligible records, and even time that would normally be unpaid will usually receive some overtime premium if marked as overtime.
Because the over 40 average wage option calculates the average pay over a week’s worth of time, it is important that the “First day of week” option is set correctly so that the calculation incorporates the records for the proper week.
To demonstrate how the over 40 average wage option works, we can use the same record set as we used with the over 8 option and add just a couple of records. Presume a person has the following time records for the week, that all of the work counts toward overtime pay calculation, that the Multiplier value is 1.5 (time-and-a-half) and that the week begins on Monday:
Sunday:
- 3 hours in guaranteed rate work: $24.00
Monday:
- 3 hours in piece rated work:$4.79.
- 2 hours in guaranteed rate work: $16.00
- 3 hours in productivity-based work: $18.72
- 1 hour in unpaid programmed time: $0.00. This is the hour that is marked as overtime.
Tuesday:
- 2 hours in piece rated work: $8.01
The pay for the overtime hour of work would be $2.16:
- Total non-overtime earnings: 4.79 + 16 + 18.72 + 8.01 = 47.52
- NOTE: The $24.00 earned on Sunday is not included because the week is set to begin on Monday, therefore those hours are not part of the week in which the overtime occurred.
- Total overtime-eligible hours: 3 + 2 + 3 + 1 + 2 = 11
- 47.52 / 11 = 4.32 * .5 = 2.16
If we take the exact same time records but set the week to start on Sunday, the average will include more time and earnings, and the pay for the hour of overtime would $2.56:
- Total non-overtime earnings: 24 + 4.79 + 16 + 18.72 + 8.01 = 71.52
- Total overtime-eligible hours: 3 + 3 + 2 + 3 + 1 + 2 = 14
- 71.52 / 14 = 5.1085 * .5 = 2.56
